With the depletion of natural resources, fuel cell technology has gained more and more attention as an alternative to conventional forms of energy. In fact, fuel cells can generate a significant amount of electricity from a catalyst-facilitated chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen ions in a cell.
The majority of fuel cells make use of platinum catalysts, but the recent surge of interest in renewable resources has triggered a corresponding increase in the need for developing new type of fuel cell catalysts that are renewable, energy-efficient, and low-cost at the same time. As a result, graphene has been regarded as a possible alternative to replace the expensive platinum. However, due to its low electrochemical performance, the use of a non-metal element turned out to damage graphene crystals.
On March 22, a team of scientists, led by Prof. Jong-Beom Baek (School of Energy and Chemical Engineering)announced that they have successfully developed a low-cost and reusable electrode material for fuel cells by selectively plating antimony with graphene through a mechanochemical process.
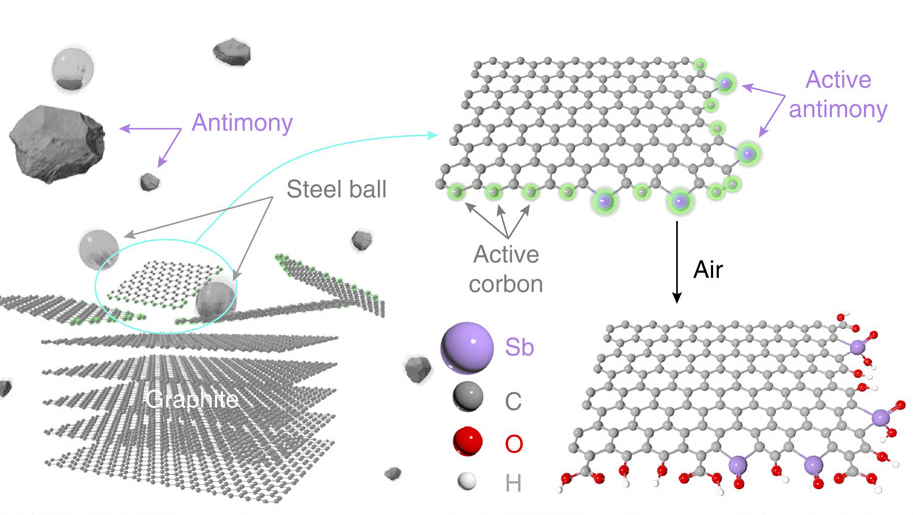
A schematic showing the SbGnPs structure, being prepared by ball-milling graphite in the presence of solid antimony (Sb) in a ball-mill crusher.
In this study, the research team plated the edges of graphene nanoplatelets (GnPs) with semimetal antimony (Sb) using the low-cost and scalable ball-milling technique to overcome the limitations of the non-metal materials.
According to Prof. Baek, this Sb-doped GnPs may be a significant breakthrough in fuel cell technology as it displays zero loss of electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction even after 100,000 cycles.
Prof. Beak’s says, “We expect that this unique material will provide new insights and practocal methods for designing stable carbon-based electrocatalysts and accelerate the commercialization of graphene, thereby contributing greatly to the supply of industrial materials..”
The research findings were first appeared online in Nature Communications, a bi-monthly scientific journal published by the Nature Publishing Group on May 22, 2015.
Journal Reference: In-Yup Jeon, Min Choi, Hyun-Jung Choi, Sun-Min Jung, Min-Jung Kim, Jeon, Jeong-Min Seo, Seo-Yoon Bae, Seonyoung Yoo, Guntae Kim, Hu Young Jeong, Noejung Park & Jong-Beom Baek, “Antimony-doped graphene nanoplatelets.” Nature Communications (6), Article Number: 7123.