The portrait of Mookpododo—an ink on-silk painting of grapes featured on the genuine Korean ₩50,000 bill—radiates a bright fluorescent green, an effect achieved through security ink that is visible under ultraviolet (UV) light. This feature remains concealed from the naked eye and is intended for use by professionals in financial institutions and other high-security environments.
In a significant advancement in the field of anti-counterfeiting technology, Professor Jiseok Lee and his research team in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST have developed a new hidden anti-counterfeiting technology, harnessing the unique properties of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs).
“The technology we have developed holds significant promise in preventing the counterfeiting of valuable artworks and defense materials, particularly in scenarios where authenticity must be verified against potential piracy,” Professor Lee explained.
The team leveraged the inherent disadvantage of AgNPs, which tend to discolor upon exposure to UV light, to create a controlled color development process. By trapping silver nanoparticles within a polymer matrix, researchers can manipulate particle size and, consequently, the color emitted under UV light. Larger polymer nets yield silver nanoparticles that appear yellow, while smaller nets produce a red hue, allowing for precise control of the resultant colors based on ingredient combinations.
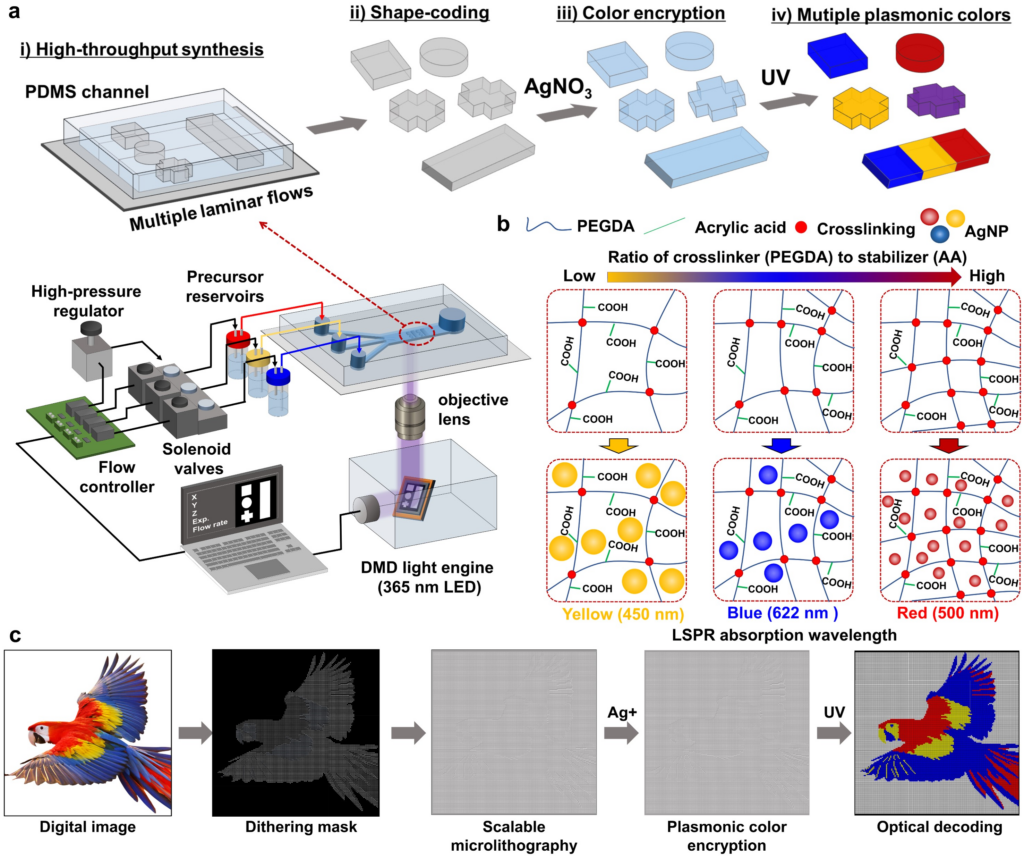
Figure 1. High-throughput synthesis of multiple plasmonic colored microarchitectures via digital mask flow micro-lithography systems.
Using these high-molecular structures as pixels, the research team successfully crafted high-resolution color images. Utilizing an automated photo-etching technique, they reduced the fabrication time to one-tenth of traditional methods, producing an image of a parrot larger than a standard business card in just 30 minutes. This digital process allows for flawless color printing, with precise control over saturation and tone.
In addition to images, anti-counterfeiting data can be discreetly embedded in arrangements of polymer structures that resemble red, yellow, and blue barcodes. The color response varies with UV exposure time, allowing for the storage of temporal information within the barcode structure. This innovative approach enables information storage capabilities to increase over 1,000-fold compared to conventional methods, with a potential for unlimited data encoding by arranging barcode particles without additional synthesis.
To enhance the reliability of this technology, the research team developed an artificial intelligence algorithm capable of analyzing barcode authenticity. This AI system boasts a remarkable reliability rate of 98.36%, distinguishing genuine barcodes from counterfeit ones by assessing material composition, UV exposure duration, and barcode integrity.
“The simplicity of the manufacturing process and the reproducibility of colors present a substantial opportunity for the advancement of information encryption systems, particularly in anti-counterfeiting applications,” stated Byungcheon Yoo, the lead author of the study.
The groundbreaking findings from this research were published in the online version of Advanced Materials on November 20, 2024. This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Journal Reference
Byungcheon Yoo, Chaeyeong Ryu, Seunghwan Lee, et al., “High-Throughput Multiplexed Plasmonic Color Encryption of Microgel Architectures via Programmable Dithering-Mask Flow Microlithography,” Adv. Mater., (2024).