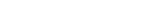A groundbreaking technology has been developed by Professor Youngkook Kwon’s team in the School of Chemical Engineering at UNIST, aiming to significantly improve the performance of an electrolyzer used for hydrogen generation. This advancement brings us a step closer to the commercialization of green hydrogen production technology.
The team has successfully created a novel in-situ, ionomer-free catalyst-coated membrane (m-CCM) fabrication method, which enables the synthesis and integration of a catalyst layer between the anion exchange membrane (AEM) and the gas diffusion layer without the need for anion exchange ionomers. This innovative approach surpasses the limitations of conventional membrane electrode assembly (MEA) fabrication methods.
Figure 1. The first facile in-situ, ionomer-free catalyst-coated membrane (modified CCM; m-CCM) fabrication method, developed by the research team.
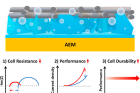
Utilizing a platinum group metal-free benchmark anode catalyst, the Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzer (AEMWE) fabricated through the m-CCM method has demonstrated remarkable performance superiority over its MEA counterparts. The m-CCM method optimizes the interfacial resistance, maximizes catalyst utilization, and establishes intimate contact, enabling an industrially relevant current density of 1 A cm–2 at a moderate cell voltage of 1.79 Vcell. Furthermore, it exhibits exceptional durability, withstanding over 200 hours of continuous electrolysis at 50 °C in 1 M KOH electrolyte.
Moreover, the AEMWE achieves a current density of 500 mA cm–2 at a cell voltage of 1.913 Vcell and showcases a low degradation rate of 0.58 mV h–1 during 260 hours of continuous electrolysis at a current density of 250 mA cm–2, all while operating at 50 °C in ultrapure water.
The key to this improved performance and stability lies in the direct growth of the catalyst layer, eliminating the need for ionomers commonly used in the manufacturing process of the membrane electrode assembly. By excluding ionomers and directly growing the catalyst layer, the m-CCM method optimizes the membrane-catalyst-support interface, resulting in enhanced performance and stability.
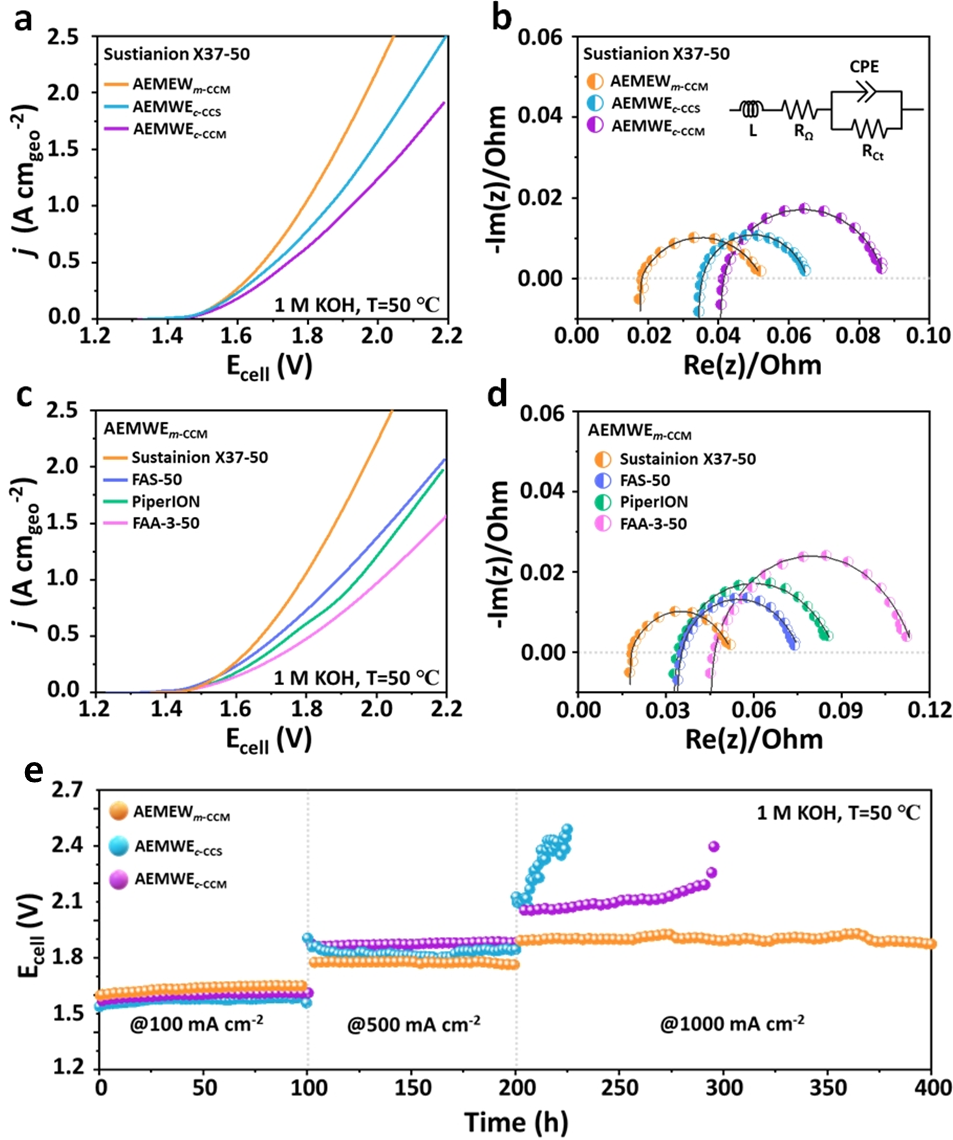
Figure 2. Electrochemical analysis of AEMWEs in 1 M KOH at 50 °C., as well as the long-term stability test of AEMWEs fabricated using an m-CCM, a c-CCS, and a c-CCM with Sustainion X37-50 at sequentially increasing constant current densities of 100, 500, and 1000 mA cm–2.
“Securing both performance and stability of the water electrolyzer is crucial for the commercialization of green hydrogen production technology,” stated Professor Kwon. “By addressing the challenges associated with the membrane electrode assembly, we are accelerating the realization of a hydrogen economy.”
The study findings, published in the online version of ACS Energy Letters on October 13, have been selected as the cover article and published on November 10, 2023. This groundbreaking research was made possible with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), and the Energy Technology Development Project of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE).
Journal Reference
Tae-Hoon Kong, Pandiarajan Thangavel, Seokmin Shin, et al., “In-Situ Ionomer-Free Catalyst-Coated Membranes for Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzers,” ACS Energy Lett., (2023).