From investigating predator bacteria and studying organisms at the molecular level to understanding host responses and looking for effective new drugs, scientists in Asia are making big strides. This includes Professor Robert Mitchell in the Department of Biological Sciences within the College of Information and Biotechnology at UNIST. Asia Research News surveyed institutions in Asia to learn about their latest contributions to antimicrobial resistance research.
Korea
Working just south of Seoul, Soojin Jang is the group leader of Institut Pasteur Korea’s Antibacterial Resistance Research Laboratory. She is leading her team’s efforts to study bacterial physiology and resistance mechanisms. Their aim is to use this knowledge to develop new screening systems for identifying small molecules and natural compounds that can be used against drug-resistant organisms.
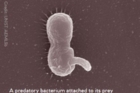
Further southeast, Robert Mitchell is studying a type of bacteria that destroys other organisms. A biological scientist at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) in Korea, he and his colleagues have found that these ‘predatory bacteria’ not only kill other pathogens, but can also remove their DNA, including their antibiotic resistance genes. In his most recent study, Mitchell found that the predatory bacterium Bdellovibrio baceriovorus HD100 was active against two groups of antimicrobial-resistant pathogens under simulated microgravity conditions. The findings illustrate its potential for treating biofilm-covered surfaces in spacecrafts. Asia Research News covered their previous work in 2017.
Japan
At Kyoto University in Japan, structural biologist So Iwata has been using X-ray protein crystallography to investigate how specialized membrane channels, called transporters, remove antimicrobial drugs from inside bacterial cells, saving them from their deadly effects. “We found that these nanoscale molecular machines change their shapes to pump antibiotics out of the bacteria,” he explains.
Osaka City University (from Apr 2022 Osaka Metropolitan University) dermatologist Toshiyuki Ozawa has been looking into photodynamic therapy. His team uses a light-sensitive substance, which reacts with a certain wavelength of light to produce reactive oxygen that selectively kills malignant tumors and bacteria. Unlike antibiotics, the therapy does not produce drug-resistant bacteria.
Nepal
At Kathmandu’s Global Institute for Interdisciplinary Studies, Suraj Bhattarai, an InterAcademy Partnership (IAP) Young Physician Leader, has demonstrated the high burden of serious bacterial infections and multidrug-resistant bacteria on community and hospital deaths in low- and middle-income countries, including Nepal. His research highlights the importance of health-facility and community-level surveillance of antimicrobial resistance.
Hong Kong
Biomedical scientists Xin Deng and Jian Yan at the City University of Hong Kong (CityU) have identified gene regulatory proteins, called transcription factors, that are involved in making the bacterium Pseudomonas syringae harmful against a wide variety of plants. In one of their most recent studies, they revealed how these transcription factors bind to genes in order to activate them. Their research could facilitate the development of new drugs against the bacterium.
Also at CityU, veterinary bacteriologist Sheng Chen has been investigating how a bacterial gene has evolved to resist tigecycline, a last-resort antibiotic. His research, which involved studying thousands of bacterial strains collected in China over a quarter of a century, suggests the gene may have originally come from a Flavobacteriaceae ancestor and was then transferred to other bacteria. He and his team hope that blocking the mechanism that facilitates the gene’s transmission could lead to new treatment strategies.
Singapore
Andrea Lay Hoon Kwa and her team at Duke-NUS Medical School/ Singapore General Hospital, are investigating strategies for managing critically ill patients with difficult-to-treat infections. Using a technique they developed, ineffective antibiotics gain new potency when used as a combined therapy. Additionally, they are looking into optimal prescriptions and combining antibiotics with harmless, naturally occurring viruses that infect bacteria.
At the Agency for Science, Technology, and Research (A*STAR)’s Infectious Diseases Labs, scientists are looking for ways to develop strategies against treatable and antibiotic-resistant pathogens. The team at Pablo Bifani’s Antimicrobial Resistance Lab, for example, is looking for special viruses, called bacteriophages, that can be used against antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. Amit Singhal’s Bacterial Immunopathology Lab is investigating the mechanisms behind the inflammatory responses caused by major infectious diseases in Southeast Asia, like tuberculosis and dengue. At the Antifungal Resistance Lab, Wang Yue is profiling and characterizing the mutations that lead to resistance. He and his team hope their work will lead to the identification of new drug targets. Matthew Tay’s research at the Antimicrobial Biologics Lab is focused on finding ways to develop antibodies that can be used as adjunct therapies against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Finally, Stefan Oehlers at the Bacterial Pathogenesis Lab is using infected zebrafish to rapidly test antibiotic toxicity and their bioavailability to bacteria.
Asia Research News
W: https://www.asiaresearchnews.com/
E:info@researchsea.com
Twitter: @ResearchSEA
Story Source
Materials have been provided by Asia Research News. This story has been featured in the Asia Research News 2022 magazine.
Notes for Editors
This press release is made available courtesy of Asia Research News and the research institutions featured.