A team of researchers from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, jointly led by Professors Sung-Yeon Jang, Jungki Ryu, and Ji-Wook Jang, in collaboration with Professor Sang Kyu Kwak from Korea University, have achieved remarkable advancements in the stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells. Their groundbreaking work not only paves the way for the commercialization of perovskite solar cells (PSCs), but also offers significant potential in green hydrogen production technology, ensuring long-term operation with high efficiency.
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have garnered attention due to their reduced toxicity and broad light absorption capabilities, making them highly promising for photovoltaic applications. However, the presence of inherent ionic vacancies in tin-lead halide perovskites (TLHPs) has posed challenges, leading to accelerated device degradation through inward metal diffusion.
To address this challenge, the research team developed a chemically protective cathode interlayer using amine-functionalized perylene diimide (PDINN). By leveraging its nucleophilic sites to form tridentate metal complexes, PDINN effectively extracts electrons and suppresses inward metal diffusion. The novel solution-processed PDINN cathode interlayer has showcased remarkable performance in stabilizing TLHP-based photovoltaic (PV) and photoelectrochemical (PEC) devices.
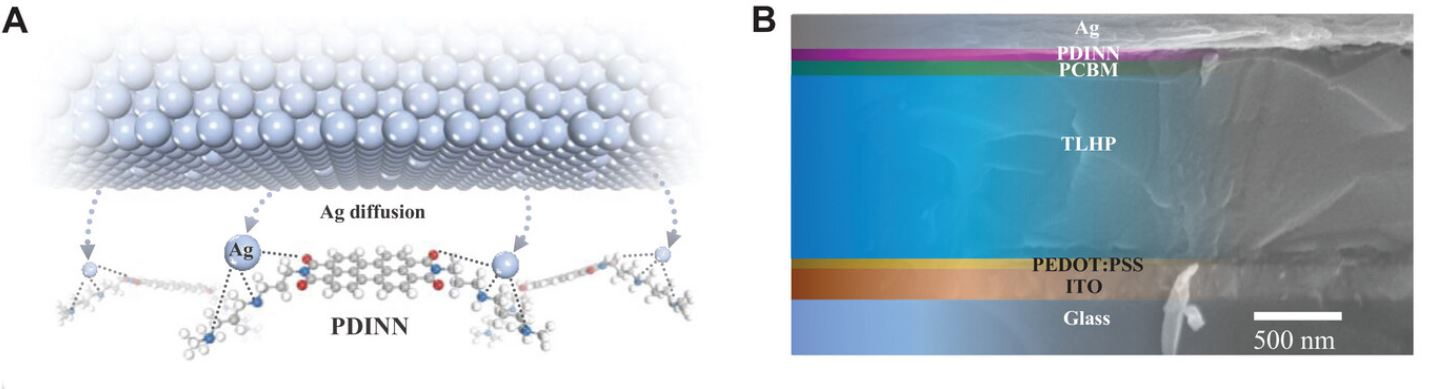
Figure 1. a) Illustration of the chemical interaction between PDINN and metal atoms. b) Cross-sectional SEM image of a PV device.
The PV device achieved an impressive efficiency of 23.21%, with over 81% retention after 750 hours of operation at 60 °C, and more than 90% retention after 3100 hours at 23 ± 4 °C. Additionally, the TLHP-based PEC devices, coupled with biomass oxidation, exhibited a record-high bias-free solar hydrogen production rate of 33.0 mA cm−2, approximately 1.7-fold higher than the target set by the U.S. Department of Energy for one-sun hydrogen production.
Their innovative design of the cathode interlayer has successfully demonstrated the immense potential of TLHPs for efficient and stable photoconversion.
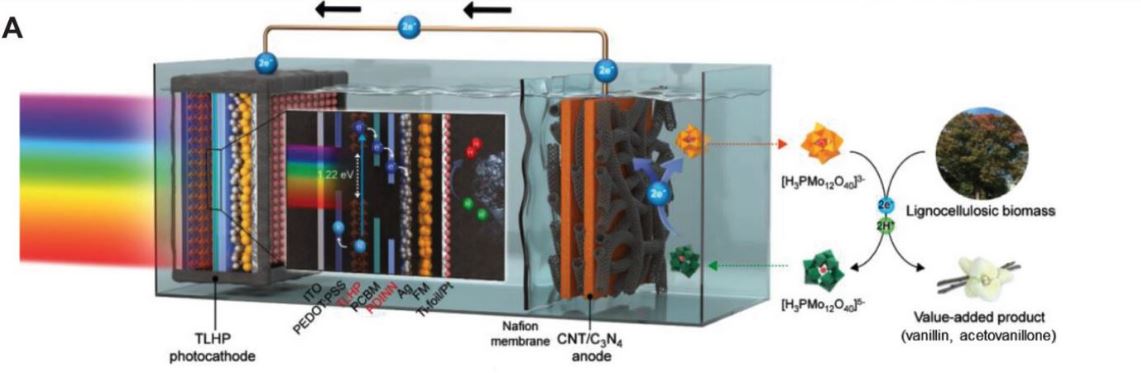
Figure 2. a) Schematic illustration of PEC device using TLHP/PDINN photocathode and CNT/C3N4 anode.
“We have dramatically increased the long-term stability of tin-lead PSCs,” explained Professor Jang. “Our goal is not only to convert light energy into electrical energy but also to develop eco-friendly methods for producing basic chemicals, such as hydrogen, which form the foundation of various industries.”
The research findings have been published online in Advanced Energy Materials on November 30, 2023. The study received support from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) under the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT).
Journal Reference
Muhibullah Al Mubarok, Yuri Choi, Rashmi Mehrotra, et al., “Efficient and Stable Tin–Lead Perovskite Photoconversion Devices Using Dual-Functional Cathode Interlayer,” Adv. Energy Mater., (2023).