Ammonia is emerging as a promising energy source to achieve carbon neutrality due to its inherent carbon-free nature. A recent study, led by Professor Hankwon Lim in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering and the Graduate School of Carbon Neutrality at UNIST, has evaluated the feasibility of ammonia-based power generation through techno-economic and carbon footprint analyses. The research focuses on an integrated system combining ammonia decomposition and phosphoric acid fuel cells.
The study, conducted using a commercial process simulator, unveils significant findings regarding the efficiency and economic viability of utilizing ammonia in power generation systems. Results indicate an impressive energy efficiency rate of 46.7% within the designed power generation process.
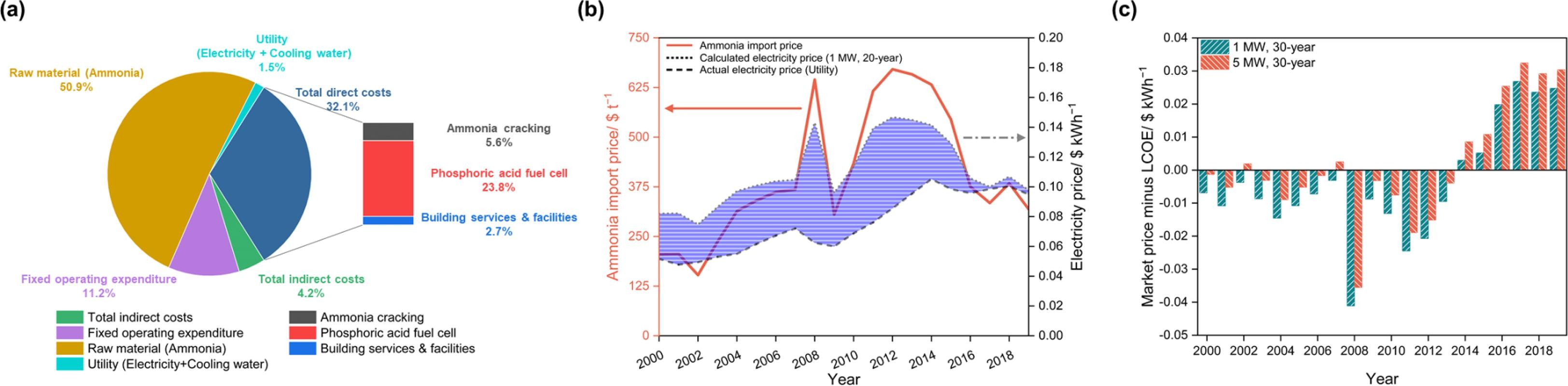
Figure 1. (a) Cost breakdown of the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) in the case of industrial electricity prices (20-year average of 0.075 $ kWh−1), (b) the change in ammonia import prices, electricity prices, and calculated LCOE in the ammonia-based power generation using phosphoric acid fuel system, and (c) difference between industrial electricity price and calculated LCOE in the system with longer plant operating period and scaled-up capacity.
Through comprehensive economic analysis, the research team identified an upper limit for ammonia pricing at 421.3 $ tNH3–1 that allows competitive pricing against industrial electricity rates—a crucial factor in determining market competitiveness.
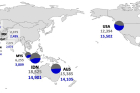
To further optimize ammonia imports into the Republic of Korea (KOR), five distinct scenarios were established based on historical data from the top ten exporting countries. Using the Monte Carlo method for ammonia production costs and carbon dioxide emissions in each nation, researchers optimized import quantities while minimizing overall emissions.
The results demonstrate that if solely reliant on carbon-based ammonia imports, carbon intensity ranges between 0.707–0.736 kgCO2-eq kWh−1—exceeding KOR’s average value over a 20-year period. However, achieving a ratio of over 78% of carbon-neutral ammonia (Scenario 4) can make both environmental and economic aspects more favorable.
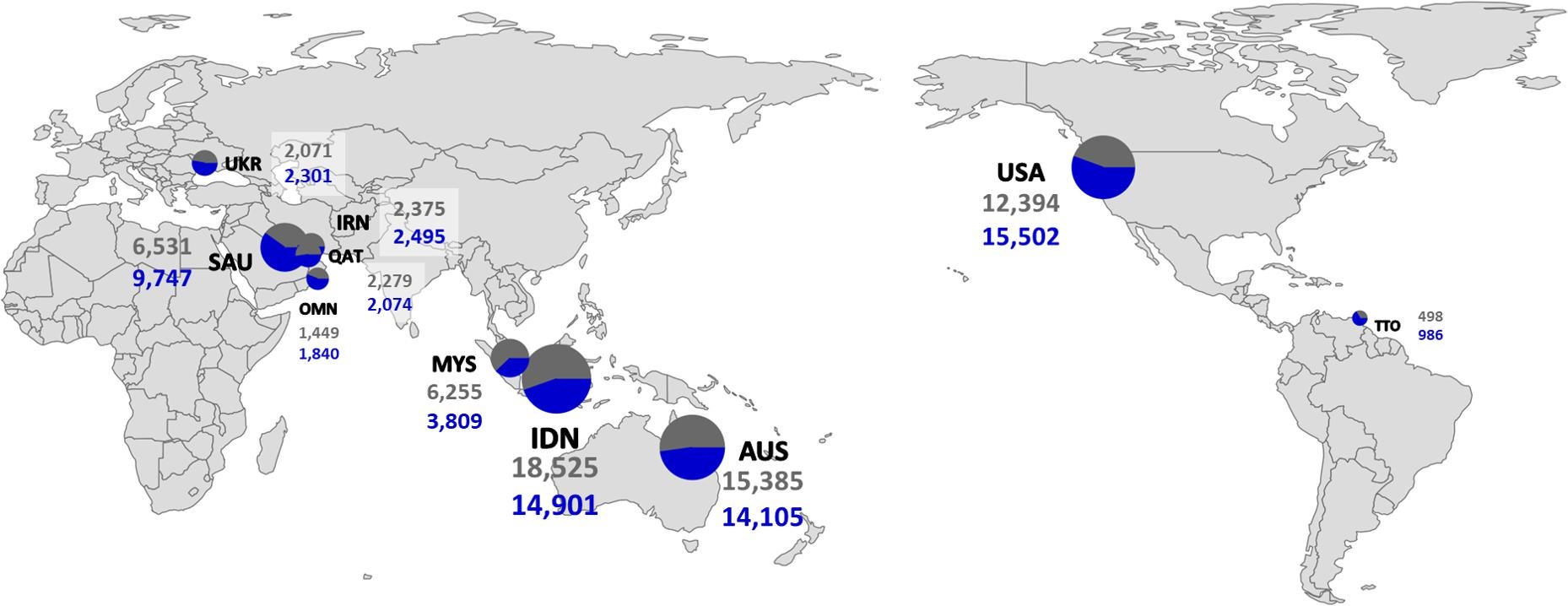
Figure 2. Optimization results for importing ammonia from the top ten exporting countries (Scenario 3); The circle size represents the amount of imported ammonia and the color represents the ratio of carbon-based to carbon–neutral ammonia (gray indicates carbon-based ammonia and blue indicates carbon–neutral ammonia). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
According to the research team, their findings provide valuable insights into optimizing ammonia exports and reducing carbon intensity. By adopting a holistic approach that encompasses all stages of the supply chain, significant progress can be made towards sustainable energy solutions.
“Our study sheds light on the immense potential of ammonia as an energy source,” said Professor Lim. “We have analyzed costs and greenhouse gas emissions while considering different commercialized methods of producing ammonia. Although renewable energy sources were not part of this particular study, our findings offer crucial insights into enhancing ammonia exports and promoting sustainability.”
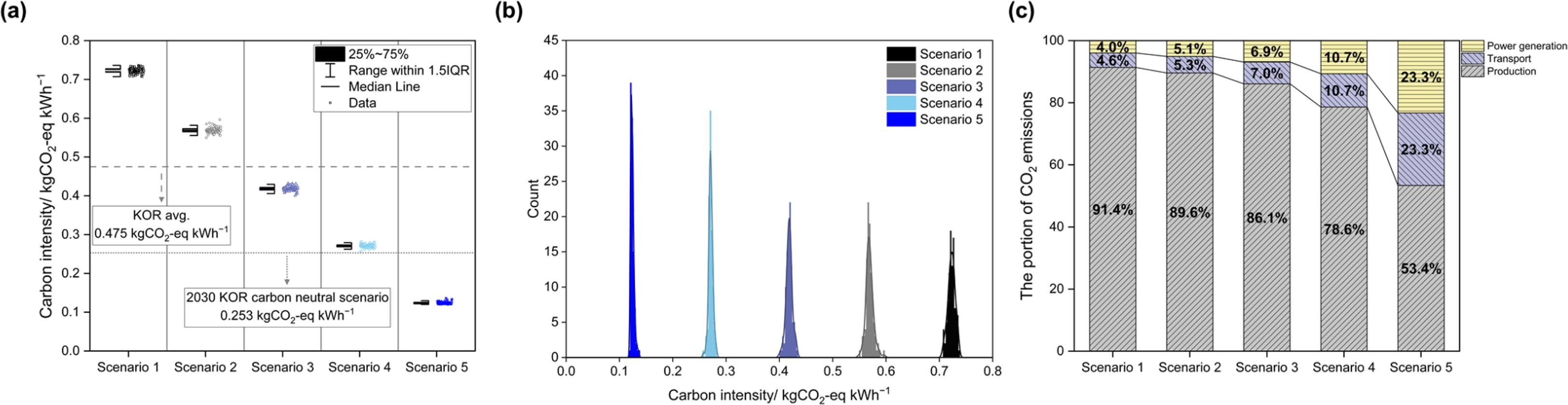
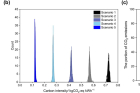
Figure 3. Optimization results for the ammonia-based power generation system using a phosphoric acid fuel cell in terms of carbon intensity considering production, transportation, and decomposition of ammonia for each scenario: (a) bar chart and 100 data points, (b) histogram and kernel density estimation distribution, and (c) percentage of emissions attributed to production, transportation, and power generation.
The study findings have been published ahead of their official publication in the online version of Chem. Eng. J. on May 13, 2023. This work has been supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the Carbon Neutrality Demonstration and Research Center of UNIST, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy and Korea (MOTIE), and Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology (KEIT). Their findings are expected to contribute to advancing the understanding and utilization of ammonia as a viable option for decentralized power generation systems.
Journal Reference
Dongjun Lim, Jong Ah Moon, Yeong Jin Koh, et al., “Expansion and optimization of ammonia import to the Republic of Korea for electricity generation,” Chem. Eng. J., (2023).